


|
||
|
||
Microsoft and Google almost always land on the list of most-phished brands, and that is not surprising given their huge market presence. And phishers are often the most likely threat actors to bank on the brands’ popularity for the success of their attacks.
Malwarebytes Labs, in fact, dove deep into a new campaign targeting Microsoft advertisers. The threat actors used malicious Google ads to steal the login information of users of Microsoft’s advertising platform.
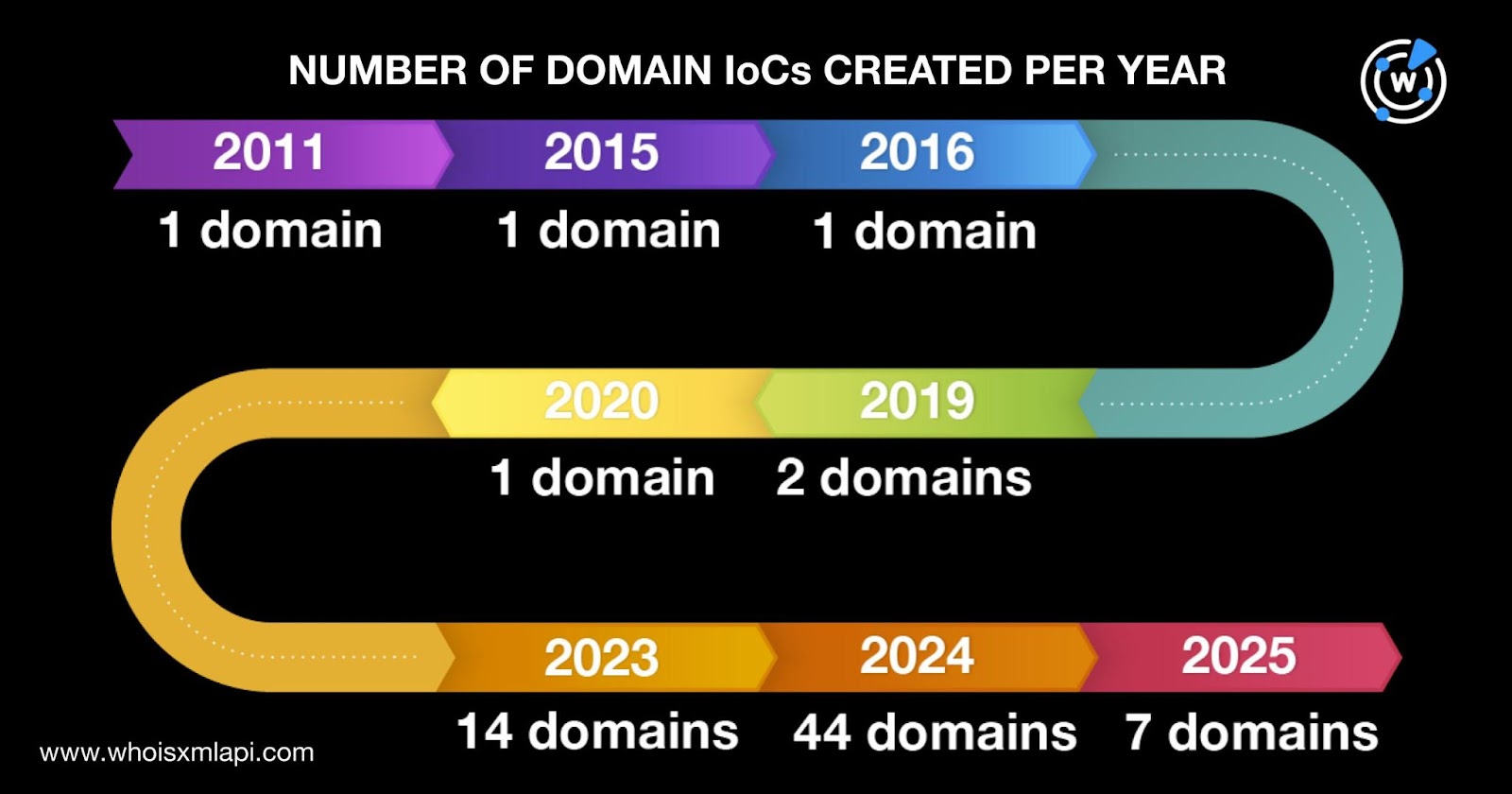
The researchers identified 97 domains as indicators of compromise (IoCs) in their report. WhoisXML API expanded the current IoC list using our extensive collection of DNS intelligence and uncovered additional connected artifacts, namely:
A sample of the additional artifacts obtained from our analysis is available for download from our website.
We began our investigation by querying the 97 domains identified as IoCs on Bulk WHOIS API. The results showed that only 71 of the domains had current WHOIS records. Based on the data we obtained, we found that:
While two of the domains did not have current registrar information, the remaining 69 were spread across 20 different registrars. Hostinger Operations was the top registrar, accounting for 20 IoCs. Sav.com took the second spot with nine domains. NameSilo placed third with eight IoCs. In fourth place was Realtime Register with seven domains. INWX, Namecheap, and Squarespace Domains tied in fifth place with three IoCs each. Hosting Concepts, NiceNIC, and Tucows shared the sixth place with two domains each. Finally, Cloud9, Dynadot, Internet Domain Service, Name SRS, Orbis, PDR, REGTIME-RU, Virtua Drug, Web Commerce, and 阿里云计算有限公司(万网) administered one IoC each.

The U.S. was the top registrant country, accounting for 19 domains. One IoC each was registered in Brazil, Croatia, Hungary, and Poland. A total of 48 domains, meanwhile, did not have current registrant country information.

We also queried the 97 domains identified as IoCs on DNS Chronicle API and found that 84 of them had DNS histories. Altogether, the 84 domains recorded 1,560 IP resolutions over time. The IoC euroinvest[.]ge, in particular, posted the oldest first IP resolution date—4 October 2019. Take a look at the DNS histories of five other domains below.
| DOMAIN IoC | NUMBER OF IP RESOLUTIONS | FIRST IP RESOLUTION DATE |
|---|---|---|
| 30yp[.]com | 32 | 29 September 2021 |
| adsadvertising[.]online | 2 | 25 May 2024 |
| blseaccount[.]cloud | 16 | 22 January 2024 |
| krakeri-login[.]com | 24 | 21 May 2024 |
| poezija[.]com[.]hr | 109 | 15 October 2019 |
IoC List Expansion Analysis Findings
We started our IoC list expansion by querying the 97 domains identified as IoCs on WHOIS History API. We uncovered 59 email addresses from the historical WHOIS records of 32 domains after duplicates were filtered out. Further scrutiny of the 59 email addresses revealed that 26 were public addresses.
A Reverse WHOIS API query for the 26 public email addresses showed that none of them appeared in other domains’ current WHOIS records.
So, we dug deeper. We queried the 26 public email addresses and found that 14 appeared in the historical records of 204 email-connected domains after duplicates and those already identified as IoCs were filtered out.
Next, a DNS Lookup API query for the 97 domains identified as IoCs revealed that they actively resolved to 25 IP addresses after duplicates were filtered out.
A Threat Intelligence API query for the 25 IP addresses showed that 16 were already considered malicious. Take a look at five examples below.
| MALICIOUS IP ADDRESS | ASSOCIATED THREATS |
|---|---|
| 104[.]21[.]32[.]1 | Attack Command and control (C&C) Generic threat Malware distribution Phishing Spam campaign Suspicious activity |
| 104[.]21[.]7[.]203 | Generic threat Malware distribution Phishing |
| 15[.]197[.]130[.]221 | Attack C&C Generic threat Malware distribution Phishing Suspicious activity |
| 172[.]67[.]203[.]159 | Attack Malware distribution |
| 34[.]76[.]205[.]124 | Attack Generic threat Malware distribution Phishing |
This post only contains a snapshot of the full research. Download the complete findings and a sample of the additional artifacts on our website or contact us to discuss your intelligence needs for threat detection and response or other cybersecurity use cases.
Disclaimer: We take a cautionary stance toward threat detection and aim to provide relevant information to help protect against potential dangers. Consequently, it is possible that some entities identified as “threats” or “malicious” may eventually be deemed harmless upon further investigation or changes in context. We strongly recommend conducting supplementary investigations to corroborate the information provided herein.
Sponsored byWhoisXML API

Sponsored byCSC

Sponsored byRadix

Sponsored byVerisign

Sponsored byDNIB.com

Sponsored byIPv4.Global

Sponsored byVerisign
