

 India's AI summit promised a Global South rethink of digital governance. Instead, a weak declaration and Delhi's accession to America's Pax Silica exposed widening power asymmetries, leaving countries like Brazil outside the real circuitry of control.
India's AI summit promised a Global South rethink of digital governance. Instead, a weak declaration and Delhi's accession to America's Pax Silica exposed widening power asymmetries, leaving countries like Brazil outside the real circuitry of control.
 At Munich's twin security gatherings, leaders warned that cyber conflict, transatlantic rifts and weaponised AI are pushing the rules-based order into a perilous transition, where deterrence falters, norms erode and digital sovereignty trumps multistakeholder ideals.
At Munich's twin security gatherings, leaders warned that cyber conflict, transatlantic rifts and weaponised AI are pushing the rules-based order into a perilous transition, where deterrence falters, norms erode and digital sovereignty trumps multistakeholder ideals.
 Project Jake invites global DNS stakeholders to test JADDAR, a privacy-respecting framework for secure access to registration data, aiming to reduce regulatory fragmentation and modernise domain governance through collaborative, policy-aligned engineering solutions.
Project Jake invites global DNS stakeholders to test JADDAR, a privacy-respecting framework for secure access to registration data, aiming to reduce regulatory fragmentation and modernise domain governance through collaborative, policy-aligned engineering solutions.
A three-decade natural experiment suggests America's centralized regulatory review fostered far greater wealth creation than Europe's precautionary principle, raising stark questions about whether importing EU-style AI rules would undermine US innovation and prosperity.
As policymakers search for an IAEA for AI, lessons from ICANN and internet governance loom large, raising questions about multistakeholder legitimacy, mission creep, technical fragmentation and whether AI demands sector-specific regulation rather than grand global architectures.
 Under ICANN's ICP-2 framework, RIR emergency operations extend beyond technical redundancy to encompass legal relocation, policy divergence and geopolitical risk, exposing tensions between operational resilience and national sovereignty in safeguarding global internet governance.
Under ICANN's ICP-2 framework, RIR emergency operations extend beyond technical redundancy to encompass legal relocation, policy divergence and geopolitical risk, exposing tensions between operational resilience and national sovereignty in safeguarding global internet governance.
 In February 1996, a libertarian myth of cyberspace and sweeping US platform immunity collided, hardwiring digital exceptionalism. Three decades on, that original sin still shields tech and AI from accountability, with legal and social consequences.
In February 1996, a libertarian myth of cyberspace and sweeping US platform immunity collided, hardwiring digital exceptionalism. Three decades on, that original sin still shields tech and AI from accountability, with legal and social consequences.
 Iran's 2026 internet shutdown was not a glitch but a trial of digital sovereignty, revealing how easily connectivity can be weaponised to silence society, concentrate state power, and fracture the promise of a global internet.
Iran's 2026 internet shutdown was not a glitch but a trial of digital sovereignty, revealing how easily connectivity can be weaponised to silence society, concentrate state power, and fracture the promise of a global internet.
 Meltnet envisions a federated internet model led by BRICS nations, combining digital sovereignty with cross-border interoperability. It challenges US-centric governance by proposing a trust-based architecture rooted in shared standards and mutual recognition.
Meltnet envisions a federated internet model led by BRICS nations, combining digital sovereignty with cross-border interoperability. It challenges US-centric governance by proposing a trust-based architecture rooted in shared standards and mutual recognition.
 Poland thwarted a large-scale cyberattack on its energy grid without disruption, offering a rare case study in critical infrastructure resilience, decentralised energy governance, and the balancing act between openness and digital security.
Poland thwarted a large-scale cyberattack on its energy grid without disruption, offering a rare case study in critical infrastructure resilience, decentralised energy governance, and the balancing act between openness and digital security.
 A 2026 outlook charts Internet governance between fear and hope, tracking cyber conflict, digital trade and taxation, shrinking rights, and global AI rivalry, while asking whether multistakeholder cooperation can still steer the network toward stability.
A 2026 outlook charts Internet governance between fear and hope, tracking cyber conflict, digital trade and taxation, shrinking rights, and global AI rivalry, while asking whether multistakeholder cooperation can still steer the network toward stability.
 Global digital policy frameworks often overlook the realities of African SMEs, imposing compliance standards shaped by mature economies and infrastructure, thereby constraining innovation, competitiveness, and inclusion in the digital economy.
Global digital policy frameworks often overlook the realities of African SMEs, imposing compliance standards shaped by mature economies and infrastructure, thereby constraining innovation, competitiveness, and inclusion in the digital economy.
 ICANN's 2026 Nominating Committee invites applications for key policy council roles that shape global Internet governance, offering leadership opportunities in domain regulation, digital rights, and multistakeholder decision-making. Deadline: 18 February 2026.
ICANN's 2026 Nominating Committee invites applications for key policy council roles that shape global Internet governance, offering leadership opportunities in domain regulation, digital rights, and multistakeholder decision-making. Deadline: 18 February 2026.
 Iran's deliberate disconnection from the global internet reveals a deeper crisis in digital governance, where state-led suppression and procedural legitimacy now threaten the foundational architecture and human rights principles of an open web.
Iran's deliberate disconnection from the global internet reveals a deeper crisis in digital governance, where state-led suppression and procedural legitimacy now threaten the foundational architecture and human rights principles of an open web.
 The gTLD race is not just about technical readiness. Governance strategy, institutional stamina, and adversarial foresight will define success in ICANN's 2026 round, where geopolitical resistance, not DNS errors, threatens survival.
The gTLD race is not just about technical readiness. Governance strategy, institutional stamina, and adversarial foresight will define success in ICANN's 2026 round, where geopolitical resistance, not DNS errors, threatens survival.
 Iran Expands Digital Dragnet After Crushing Protests
Iran Expands Digital Dragnet After Crushing Protests Africa’s Digital Darkness: Internet Shutdowns Reach Record High
Africa’s Digital Darkness: Internet Shutdowns Reach Record High Biden Administration to Back UN Cybercrime Treaty Amid Controversy
Biden Administration to Back UN Cybercrime Treaty Amid Controversy Future of .io Domain Uncertain as UK Relinquishes Chagos Islands
Future of .io Domain Uncertain as UK Relinquishes Chagos Islands NIS 2 Directive Set for Implementation with New Guidelines, But Concerns Remain
NIS 2 Directive Set for Implementation with New Guidelines, But Concerns Remain Internet Domain Shutdowns: Ineffective and Risky, Experts Warn
Internet Domain Shutdowns: Ineffective and Risky, Experts Warn Brazil Enforces Fines for VPN Use to Access Elon Musk’s Platform X
Brazil Enforces Fines for VPN Use to Access Elon Musk’s Platform X Russia Invests $660 Million to Boost Internet Censorship and Block VPNs
Russia Invests $660 Million to Boost Internet Censorship and Block VPNs Sally Wentworth Appointed as New CEO of the Internet Society
Sally Wentworth Appointed as New CEO of the Internet Society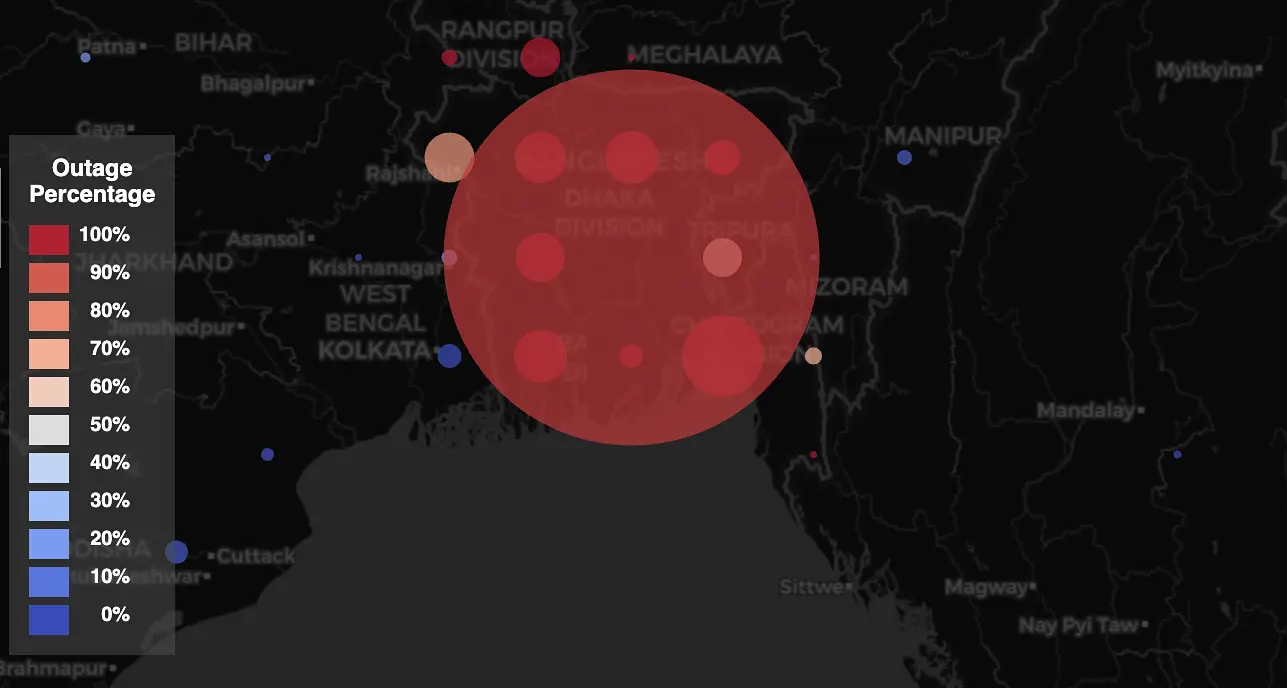 Bangladesh Faces Total Internet Shutdown Amid Violent Student Protests
Bangladesh Faces Total Internet Shutdown Amid Violent Student Protests